Thin Clients are compact devices with few moving parts and locally stored programs. They connect to servers to perform compute roles and run remote display protocols to access hard drives in secure data centers. This process instantly delivers virtual applications and desktops to end users.
Thin Client technology is widely regarded as an effective virtual desktop computing model. This is because it is a secure device where programs, applications, memory, and sensitive information are stored securely in a data center instead of the device itself. As a result, Thin Clients are viable alternatives to regular PCs for businesses that demand flexibility, energy efficiency, improved data security, and longer IT infrastructure lifespan.
What are the advantages of a Thin Client?
- Centralized IT
- Easy manageability
- Enhanced security
- Improved productivity
- Cost savings
- Remote Work Solution
To start with, it is an effective PC replacement technology that facilitates immediate access to virtual desktops and applications and offers centralized computing capabilities. Hardware and software upgrades and application changes can easily be made in the data center. Workplace productivity increases as IT teams do not need to resolve issues at the end user desktop location. Additionally, centralized backup of desktops and client access devices simplify administrator workload.
Users cannot copy information to a disk or save it to locations other than the server. Unauthorized software or applications cannot be installed on personal devices which protects companies from malware attacks and data breach attempts. All this safeguards intellectual property and ensures data privacy. Ideally, look for devices that have a Linux-based operating system and automatically receive recommended security updates. They cannot be easily tampered with as Linux is one of the most security-oriented operating systems in the market.
These endpoints represent the most affordable and environmentally sustainable solutions to date. As established, the technology is a server-based computing model that reduces TCO. This is where applications run on a remote back end server and are displayed on desktop devices. Users can access application suites from any device connected to the server without requiring IT to install applications on separate devices.
Also, having limited moving parts, low memory, and microprocessor demands, these devices consume approximately 8-20 watts compared to 170 watt PCs. This drastically reduces carbon footprint and companies can reinvest the cost savings from electricity elsewhere.
Thin Clients are effective if one wants a uniform desktop image to run across their enterprise. Many organizations may find it difficult to purchase identical configurations even if a vendor meets their demand for multiple units. Imagine a scenario where 30 different images enable support for 355 desktops and 78 servers across, say, four vendors. Thin Clients streamline this situation by delivering a universal desktop image over the network. This also tackles the process of dealing with individual variations and if a user works with a relatively unique hard drive or graphics adapter.
Consider a financial institution constructing a new building for which IT administrators need to roll out several desktops. Using conventional PCs means that they would not be able to build all of their PCs and map their drives for a hundred desktops or more. Thin Client technology is a viable option as it has minimal configuration and comes with plug and play features. The company can further gain significant cost savings from reduced levels of IT help desk support, low energy consumption, limited moving components, fanless systems, and high availability (HA).
Thin Clients play an integral role in enabling remote work solutions especially during the COVID-19 pandemic that has made it necessary for businesses to implement work from home initiatives. These endpoints are ideal for use as the foundation of a customized, enterprise remote work solution. They represent efficient, remotely managed devices that free IT departments to prioritize IT innovation for competitive advantage. Features like easy profile setups with centralized remote management and management software take the burden off IT systems management. The devices enable flexible deployment by offering both Linux and Windows firmware versions, including a variety of codecs as well as remote display protocols such as PCoIP and Blast Extreme. Furthermore, modern solutions are designed to work with any leading terminal services provider.
ClearCube provides remote access and VPN to cloud-based Thin Client solutions that allow business continuity. For instance, enterprises can leverage Teradici, VMware Horizon 7, Citrix Workspace, WVD, and Amazon Workspace with Thin Client devices to accelerate remote work practices. Companies have the freedom and flexibility to choose what suits their IT infrastructure, and there is a major benefit to this. With a uniform desktop estate, administrators can centrally and remotely manage the endpoints at the click of a mouse. Profile changes, firmware upgrades, as well as new device setup can be performed remotely with the help of an easy-to-use drag and drop interface.
When it comes to the pros and cons of Thin Clients, this technology does not have any of the latter considering the wide range of benefits it offers.
Case Studies
Why Thin Clients are good’ is a frequently asked question in the IT community. Engineered for dynamic performance, they come with top-tier configurations to suit an extensive range of use cases in multiple industries. Let’s analyze some industry-specific scenarios where you must use Thin Clients.
A Brief Insight Into Thin Clients
At some point, many companies and organizations found it difficult to keep up with managing and maintaining a PC desktop environment. We are all familiar with how PCs create clutter, overuse energy, produce heat and noise and keep IT on their toes. Consider industries like education, healthcare, and banking or intelligence agencies that continue to operate in a traditional fat client setup. The nature of work in such places indicates that delays and downtime simply cannot be afforded. However, what happens if a technical failure occurs? Administrators must visit the endpoint directly to identify the source of the problem before they can do anything else. An example is resolving virus infections where each PC is individually located.
Today, digital innovation has transformed the business world and companies are expected to keep up or fall behind the competition. Organizations are showing a growing interest in IT resources that enable them to promote simplicity and manage several users with ease. More importantly, any solution that minimizes IT threats and problems and allows companies to focus on business strategy is a winner. This is where Thin Client computing comes in.
Empower Work From Anywhere
History of Thin Clients
ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer) was one of the earliest computers to be made for the US Army to solve general numerical problems. With time, the need to shift from full-sized PCs to lightweight devices that can sit on a desk arose, and Thin Client technology was born.
The first slim clients were used to interface with mainframe computers, and these mainframes would store information and programs. Lean clients were introduced to the market right at the beginning of the big PC boom in the 80s. Back then, businesses preferred standard computers because of the machines’ emphasis on localized processing. Hobbyists, technicians, and professionals alike utilized PCs by the dozen, and the limitations of using these systems were not identified at that time. As workloads became more complex, administrators realized that the process of individually installing and updating software and operating systems on each PC was not worth the effort. Eventually, these programs became outdated as well.
Tim Negris coined the term ‘Thin Client’ in 1993, and he envisioned these devices as affordable solutions with smart and durable designs that could replace costly PC hardware. In the late 90s, businesses began accepting the idea of using these endpoints to support their IT infrastructure. A key reason is computers were hardly viewed as separate machines by then as enterprises recognized the potential of connecting devices together to create dynamic computing systems. Organizations began adopting Thin Client technology where users could access data through a central server and virtualized desktops with time, location, and device independence.
Slim client computing evolved into a mature technology over the years as better graphics and security features were added to optimize endpoint performance and support even more advanced workloads. Vendors began adding multiple layers of security to safeguard Thin Clients from ransomware, virus, and malware attacks, and to preserve data integrity.
Also, the ability of these devices to properly and completely render graphics-intensive applications was previously limited. Most graphically intense use cases still present a challenge for lean clients because they include applications like AutoCAD, 3D drawing programs, and animation tools. Administrators can cater to these at the host server with the help of GPU cards, hardware acceleration, and workstation cards. For instance, ClearCube PCoIP Host Cards deliver powerful high definition dual and quad monitor video performance. Moreover, modern Thin Client configurations now come with CPU and low energy chip sets to boost both graphical and power efficiencies.
Thin Client Architecture In Detail
You may have come across the question ‘what is Thin Client architecture’ as an oft-repeated one in the IT community. It is essential to understand how a Thin Client works, and for this, we must examine its hardware and software components.
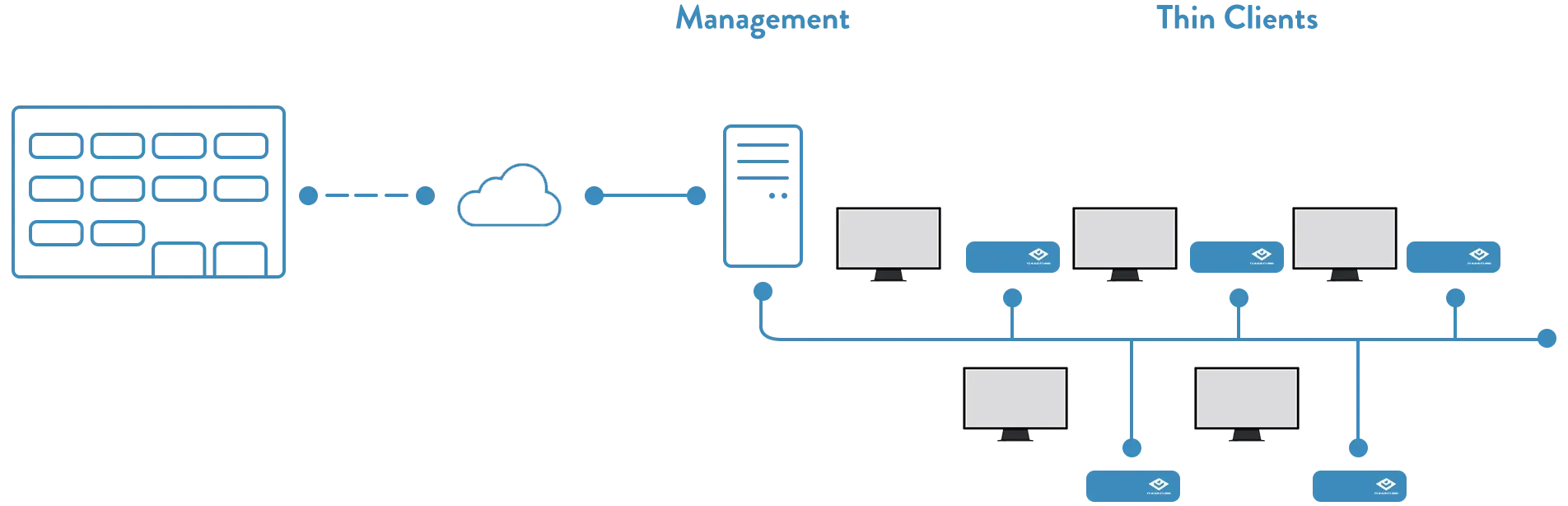
Thin Client Hardware
As mentioned previously, Thin Clients include hardware with low energy processors, memory, and limited moving parts, and they offer better performance in demanding conditions compared to traditional PCs. The hardware of these slim devices is designed to a network to a powerful terminal server. Furthermore, a lean client is normally one of many network computers which share computation needs by utilizing the resources of a single server. Users interact with a Thin Client device as if it is a full PC, even though all files and applications are stored on the server. It takes minimum hardware to boot up the primary OS and connect to the server.
Thin Client Software
Thin Client technology streamlines and simplifies desktop endpoint devices by minimizing software footprint on the client side. It consists of a small operating system (OS) that significantly decreases client-side setup and overall administration. The software allows the device to boot and connect it to the Thin Client server. Typically, the process begins with booting the OS after which the client receives the IP address and sets other variables. Next, the system connects to the server-side computing through industry-standard products or protocols such as VMware, Citrix, RDP, and browser-based connectivity. Users then log into the server using server-side credentials. In this scenario, they work on the server OS and not the local OS, which means that they use the former’s CPU, RAM, and HDD.
Notably, Thin Client solutions facilitate cloud access and this eliminates the need for a large set of data storage, local user applications, and system assets. In this way, a good portion of software workload execution is delegated to a secure data center which centralizes different elements for increased visibility, transparency, and scalability. Examples include information recovery, user utilities, and desktop repurposing functions.
Thin Client For Financial Institutions
Financial institutions need to abide by strict laws and regulations at all times. Professionals in this line of work implement roles like trading stocks and mortgage underwriting that are often the backbone of an economy. Hence, they depend on solid IT infrastructure to deliver reliable access to real-time data and meet customer needs. Even then, these professionals deal with massive numerical databases on a daily basis. In this scenario, there are far-reaching consequences of using PCs to manage workloads: compromised workstation security and performance.

As a result, adhering to core security compliance policies and maximizing uptime are top priorities. In order to achieve this, the key is to centrally manage and deliver key applications and banking systems to users. Why is this so?
Imagine a virtualized workplace where all data, applications, and desktops remain secure in a data center. In this scenario, information is not distributed to individual workstation PCs. Instead, it is saved in a central location which users can access anywhere and anytime. For example, banking officers often undertake travel to meet clients or prospects and deliver a briefing on their products. These users are no longer bound to desktop computers that demand time-consuming local maintenance, patching, and support. IT can use management software to configure connection settings based on username, department or the Thin Client supporting the VDI environment. In this way, the administration involved with managing roaming users is minimized.
On-site professionals also benefit because this simplifies common activities such as performing financial documentation and managing customer profiles. Also, IT can easily create a standardized client environment with remote management from the back office, front office, and head office. This increases the availability, operational continuity and data integrity of the overall IT environment in banks and trading floors where safeguarding quantitative data drives business success.
Tip 1: ideally, select Linux-based terminal devices to fulfill rigorous security mandates in finance. An equally important decision is the remote desktop protocol like VMware® Horizon® Blast, PCoIP, Citrix HDX and Microsoft® Windows® RDP that communicates with terminal servers. The good thing: these endpoints come with many flavors of operating systems which can be used for business-critical applications without sacrificing the benefits of centralized and holistic management.
ClearCube’s CD8851 model works well in this sector. The device supports ClearCube Cloud Desktop OS, Windows® 10 IoT, and Linux® operating systems. The Cloud Desktop OS also integrates optimized applications for all core remote networking protocols.
Following are a couple of examples of what this endpoint can do for IT environments in finance:
- Boost data and hardware security by removing local disks to reduce opportunities for theft and misuse.
- Implement browser-based desktop management with real-time monitoring, asset management, and job scheduling.
Tip 2: financial specialists simply cannot afford any delays or downtime in their workflows. While adopting Thin Clients is a smart and secure move, always keep a proactive backup solution to deal with unexpected tech errors. Luckily, there are many platforms which you can utilize to add to the security benefits of Thin Clients.
For example, ClearCube Sentral™ is the only virtual desktop software to facilitate IT a single interface to manage their entire infrastructure. Features like virtual desktop management, resource allocation, active health monitoring, and blade switching and sparing allows users to achieve server-level availability for their devices. The dashboard keeps administrators updated about the status of their IT environments by monitoring and displaying information related to servers, desktops, virtual machines, Blade PCs and Thin Clients. All this delivers up to 99.9% uptime in time and mission-critical workspace like financial institutions. Based on the metrics provided by Sentral, administrators can always configure the VDI clients to perform at the optimal level.
Thin Clients Empowering Educational Institutions
In this digital era, organizations are showing a growing interest in more secure, efficient and cost-effective IT solutions. This is especially so, considering that expensive PCs and their high TCO make it difficult for businesses to stay within budget. The same goes for educational institutions that impart knowledge and skills to prepare students for the practical world. So, it is important for students and teachers alike to have readily accessible technology that facilitates a dynamic learning environment.
Today, using PCs is questionable in academic institutions where activities like annual enrollments increase the user count. After all, updating computers with the latest software and programs is a time-consuming process and one that affects productivity. This can contribute to poor academic performance and ultimately, unsatisfactory results. Hence, it makes sense to consider affordable and collaborative technology like VDI that allows IT to create simple, secure and centrally manageable infrastructure. This helps teachers and students focus on important deliverables rather than having them waste time on reporting and troubleshooting IT issues.
It is also important that the administration has control of each and every computer system to ensure the best possible usage of technology for educational purposes. In the case of a traditional PC environment, it would require institutions to install various software on each system which enhanced the complexity of the process. On the other hand, Thin Client technology gives the administrator complete control of the operations on each system along with the power to limit operational capability on a particular system.
Choosing Thin Clients to support virtualization further helps schools and colleges do more with less, including:
Building Immersive Experiences
Any IT solution that makes learning more interactive is a winner. Thin Client devices offer a PC-like experience with complete multimedia and web browser support for high-demand environments. For example, ClearCube’s devices are engineered to facilitate the best possible performance in VDI deployments. These endpoints support the latest protocols like PCoIP, Blast Extreme and HDX and are optimized for modern desktop technologies including VMware, Citrix, and Microsoft. They come with multiple configuration options and are custom-crafted to meet the demands of all teacher and student groups. Let’s consider some examples.
Task-based users in primary school generally access a small set of applications and have limited computing requirements. They can go for a basic model like the Raspberry Pi 3 endpoint. This device facilitates high-performance, single monitor configurations in VMware Horizon and other VDI setups. Similarly, knowledge users at the intermediate level would need options that deliver a higher level of functionality. Models that offer basic multimedia features and provide multitasking capabilities work well for this group. Furthermore, there are versions which offer heavier processor usage and run multiple applications for power users like students conducting extensive fieldwork and research.
In any case, make a list of endpoint needs to determine if it suits a specific student or teacher user group. Remember that the ideal device is a single, comprehensive solution that provides everything from simple plug-and-play features to reliable hardware.
Achieving End-To-End Control
VDI has a clear use case for remote students. There are no client sites in an academic institution and students can access applications by logging into their virtual desktops at home or while commuting. A VDI environment supported by Thin Clients also provides quality administrative controls. In turn, this delivers secure virtual desktop computing for classrooms, laboratories, libraries, and auditoriums.
These clients also simplify instructor workload and facilitate transparency in teaching. In a learning environment, it is important to ensure that students only access the necessary coursework applications. Even then, it is challenging for teachers to track all the applications that students use.
Thin Client devices provide the flexibility to make unit-based customization depending on student profiles. This ensures that students do not waste their time accessing applications that have nothing to do with their lesson plans. Moreover, as information is stored on a central server, IT can effortlessly recover teacher files and student assignments in the event of technical failure. This allows the institution to follow its yearly timeline without any internal delays and deficits.
Healthcare
Healthcare specialists demand the same easy mobility and secure IT environment like users in other industries as they almost always make critical decisions. So, when these professionals boot up a screen from a device of their choice, the desktop presented must consistently deliver applications and data needed to serve patients. The same can be said for the increased usage of mobile devices which many professionals use for transferring patient files. As a result, these users need highly secure and reliable digital workspace, whether they are in the main hospital, a remote site, home clinic or managing EMR/EHR systems. They also demand IT solutions offering security controls that promote data integrity and safeguard sensitive patient information.

Taking this into account, the healthcare sector has special requirements where solutions must demonstrate security, reliability, responsiveness, and preparedness for integration with hospital systems. So, the nature of work in hospitals is such that centralized data and network management must be prioritized. Hence, adopting virtualization powered by Thin Client technology is a feasible consideration. This is because improvements in hardware abilities and management software and streamlining of remote display protocols have boosted its capabilities. These are crucial developments in healthcare because of the benefits it brings, including:
Mobility At Its Best
Healthcare specialists are always on the go. They are doctors who check on patients from room to room or administrative staff that manages multiple units in the same hospital. Also, medical practitioners are often contacted to deal with emergency situations even when they are off-duty. As a result, they can only work in highly accessible and flexible environments which regular PCs cannot provide.

Thin Client devices promote mobility as the information remains secure in the data center and can be accessed remotely. Users only need to connect to their personal desktops from any endpoint that is connected to the server hosting their data. Regardless of location, once they enter their credentials into that specific endpoint, they are almost instantly presented with the required remote desktop. This is a crucial feature in an industry where users making their rounds always need easy and on-demand access to critical patient information. For instance, IT must be able to configure access to roaming workflows where doctors can safely log in to desktops from roaming devices with a simple tap of a badge.
Better Patient Data Security
The need for data security cannot be emphasized enough as IT vulnerabilities are a growing concern. Cyber attacks are a major cause of IT frustration and anxiety, given the extent of loss or damage they could cause. Fortunately, Thin Client software from reliable vendors like ClearCube comes with built-in security features that maintain multiple layers of protection and are fully TAA compliant. Our endpoints deliver improved security by locking down the desktop which minimizes the risk of data hacking and phishing. This is a proactive measure against cyber crimes such as man-in-the-middle and DoS attacks.
Low-Cost and Efficient Management
It is not uncommon to find healthcare institutions that offer services with predefined operating budgets. Hence, they might want to preserve their legacy investment by looking for affordable alternatives to replacing desktop computers. Luckily, advanced technology such as ClearCube PC Repurposing Software offers a competitive and low-cost way to consolidate aging PC endpoints into Thin Client terminals which can connect to any remote computer or backend system. Users will still receive all the advantages of VDI on their PCs and save money over buying new computers or supporting products. Other benefits include:
- Simple setup and centralized management.
- Improved flexibility and security.
- Desktop future-proofing.
- A single OS for all hardware (Thin Clients, PCs, and laptops).
- Automatic client updates across the network.
- Multiple connection protocol support including VMware® PCoIP & Blast Extreme, Microsoft® RemoteFX and many more.
All this helps healthcare institutions reduce the complexity of switching to a full-fledged VDI setup especially if they are not prepared for one. This innovative ClearCube solution offers the opportunity to reinvest cost savings into other areas such as advanced patient care, better hospital facilities, etc.
A Perfect Solution For Retail
Just like the successful application of thin client solutions in the finance, education and defense sectors, this technology is rapidly gaining ground in other industries as well. Retail is one of the latest industries benefiting from thin clients in multiple ways. Organizations are able to grant their employees access to selected system functions and still maintain control and system security.
Thanks to the ‘Plug and Go’ feature of thin clients, they make the perfect choice for the retail industry and can set up new stores and offices within minutes. This is a must-have feature for every retail store, given the competitive nature of the retail industry. Customer-friendly, touchscreen-based and easy to use apps provided by thin clients makes retail training and day-to-day tasks fun and easy.

Every retail business owner understands that all the employees do not need a separate workstation or computing platform. Providing a terminal connection to the clerks to enable them to perform a selected few functions is enough. This is exactly what a thin client provides in retail business along with the following benefits:
- Rapid expansion – Poor or weak IT infrastructure may restrict your retail operations ability to add new store locations. However, you can completely eradicate such problems with Thin Clients that centralize applications and data in a single server location.
- Lower Power usage – You can expect a notable saving of electricity when using ClearCube’s Thin Clients as compared to standard computers.
- Portability. In order to accommodate variable workloads, highly portable Thin Clients terminals can be easily and conveniently transferred between locations. Hence, adding or removing workstations across several retail locations becomes easy.
- Data security. Since no important data is stored on the employee’s device, the risk of data security is greatly decreased as all the data goes to a single server location. Almost every retail operation includes processing credit cards in high volumes. So, this is an important and rather necessary feature for such businesses.
- Durability. Having a few moving parts, thin client terminals prove to be extremely durable. As every retail business faces a high number of customers and multiple staff members, wear and tear are almost guaranteed. ClearCube’s Thin Clients terminals make sure that your business operations go as fast and seamless as possible.
- Simplified IT. With Thin Clients in place, IT personnel can enjoy simpler, more convenient access to maintain dispersed technological assets from a single server.
Tip 1: ClearCube Thin Clients help you save time and resources, enjoy the flexibility and prepare for the future at the same time.
Tip 2: Enjoy ultimate security and safety against all sorts of cyber attacks, data loss, and theft. With thin clients in place, the employees at retail stores cannot install programs locally on the device, hence providing additional security and eliminating the risk of virus or malware attacks.
Tip 3: Leveraging Thin Client computing enables an administrator to run a network of user devices – such as ATMs- from a central server in retail banking. This minimizes operating costs as businesses use hardware and IT support resources more efficiently. Moreover, with reduced software maintenance, updates to apps and OS’s are analyzed, tested, and rolled out through the server, reaching all customer touch points at the same time. For companies looking to reduce carbon footprint, Thin Client devices limit onsite power consumption, something that traditional machines cannot do. Organizations can sum up Thin Clients as sustainable endpoints designed from scratch that delivers unified and consistent end-user experiences.
Concluding Remarks
The powerful, modern and intuitive experience which Thin Clients promise across industries has set new standards for customer expectations of client devices. The ultimate endpoint is always a well-connected, high security and a low-maintenance device that offers clients a convenient option to deploy virtual environments. For a personalized recommendation based on your unique business model, please contact a ClearCube expert today.


1 thought on “Thin Client Uses and Benefits Explained”
Comments are closed.